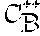
|
C++BOLD Reference Manual | 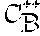
|
| Coolquest, Inc. | Home | Products | Support | About | Contact | |||
|
||||||||
| <<< Previous | CBOLD Reference Home | Next >>> |
Typically, new TPart's are not created manually. Instead, they are created by entering the component pinout in a part text file, also known as a part file. A Support Tool, pt_to_h uses the information in the part text (.pt) file to generate a C++ include (.h) file.
Like most of CBOLD, part creation is best explained by example. Below is a user-created part file, 74f07.pt:
// Part file for 74F07 Buffer Driver $PART_NAME 74F07 // hex buffer driver $FOOTPRINT SOIC14 $REF_PREFIX U $PIN_COUNT 14 $PORTS VCC5 14; // 5V power supply GND 7; A[5:0] 13 11 9 5 3 1; // inputs Y[5:0] 12 10 8 6 4 2; // outputs $ENDPORTS $ENDPART
To generate a .h file from this .pt file, the user would run pt_to_h.exe from the console as follows:
You do not typically execute pt_to_h on individual files. Instead, you execute a batch file that runs pt_to_h on all .pt files in the CBOLD parts directory. For example, see make_parts.bat, which is distributed with the CBOLD parts library.
The class declaration that pt_to_h generates from file 74f07.pt appears in file 74f07.h as follows:
class CP_74F07 : public TPart { // hex buffer driver public: port VCC5; // 5V power supply port GND; port A; // AR_BUS(5,0) // inputs port Y; // AR_BUS(5,0) // outputs CP_74F07() { ... // constructor details omitted for clarity } virtual void Register() { ... // Register() details omitted for clarity } };
This example illustrates the most commonly used features of part files. Other examples can be found by perusing the CBOLD part library. Detailed documentation is in the pt_to_h section of this reference manual.
| <<< Previous | CBOLD Reference Home | Next >>> |
| Legal | Copyright © 2007 by Coolquest, Inc. | Contact |